Security and Privacy Considerations in 'Where To Buy' Solutions
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the e-commerce industry has witnessed remarkable growth. With the advent of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions, the process of finding and purchasing products online has become more seamless and efficient. These solutions offer a bridge between the digital realm of product discovery and the real world of purchases.
This blog post delves into the diverse dimensions of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions and how they are revolutionizing the e-commerce sector. From the significance of these solutions to their role in enhancing the shopping experience, we’ll explore the core aspects that make them a game-changer for businesses and consumers alike.
The Rise of ‘Where To Buy’ Solutions
The digital age has ushered in a new era of consumer behavior. Shoppers today seek convenience, personalization, and instant access to information. They demand a frictionless path from product discovery to purchase. This is where ‘Where To Buy’ solutions enter the stage. These solutions seamlessly integrate with websites and apps, providing users with real-time, localized information on product availability, prices, and retail options.
Enhancing User Experience
In the world of e-commerce, user experience is paramount. A clunky or confusing buying journey can quickly lead to cart abandonment and lost customers. ‘Where To Buy’ solutions address this issue head-on. By streamlining the purchasing process and offering users an efficient way to find nearby products, businesses can significantly enhance the overall shopping experience.
Accessing Basic Settings
This blog post will walk you through the basic settings required to implement ‘Where To Buy’ solutions. We will explore how businesses can tailor these settings to align with their brand identity and objectives.
Button Customization
For businesses looking to integrate ‘Where To Buy’ solutions seamlessly, customization is key. We’ll discuss how to customize buttons to match a website’s aesthetics while maintaining their functionality.
Retailer Integration
A critical aspect of these solutions is their ability to integrate with a wide array of retailers. We will outline the steps involved in connecting ‘Where To Buy’ solutions with retailers, ensuring the accuracy of data and listings.
Setting Up Product Links
Successful integration of these solutions relies on effectively linking products to their corresponding retailers. In this blog post, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to create and manage product links.
Advanced Settings (if applicable)
While basic settings are crucial, advanced settings can provide a competitive edge. We’ll explore these advanced features, including analytics and geolocation, and discuss how they can be harnessed for better results.
Mobile-Friendly Configuration
With the growing use of mobile devices for online shopping, ‘Where To Buy’ solutions must be optimized for mobile users. We’ll provide insights on configuring these solutions for a mobile-friendly experience.
Testing and Troubleshooting
The journey doesn’t end with implementation. It’s essential to test and troubleshoot to ensure these solutions work seamlessly. We’ll offer guidance on effective testing strategies and solutions for common issues.
Conclusion and Next Steps
To wrap up, we’ll summarize the key takeaways from this blog post and offer insights into the next steps for businesses looking to leverage ‘Where To Buy’ solutions effectively.
In the pages that follow, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of how ‘Where To Buy’ solutions are changing the face of e-commerce and how to harness their potential for your business’s success. Whether you’re a small retailer or a global brand, these solutions have the power to elevate your online shopping experience and drive better results. So, let’s embark on this journey into the realm of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions.
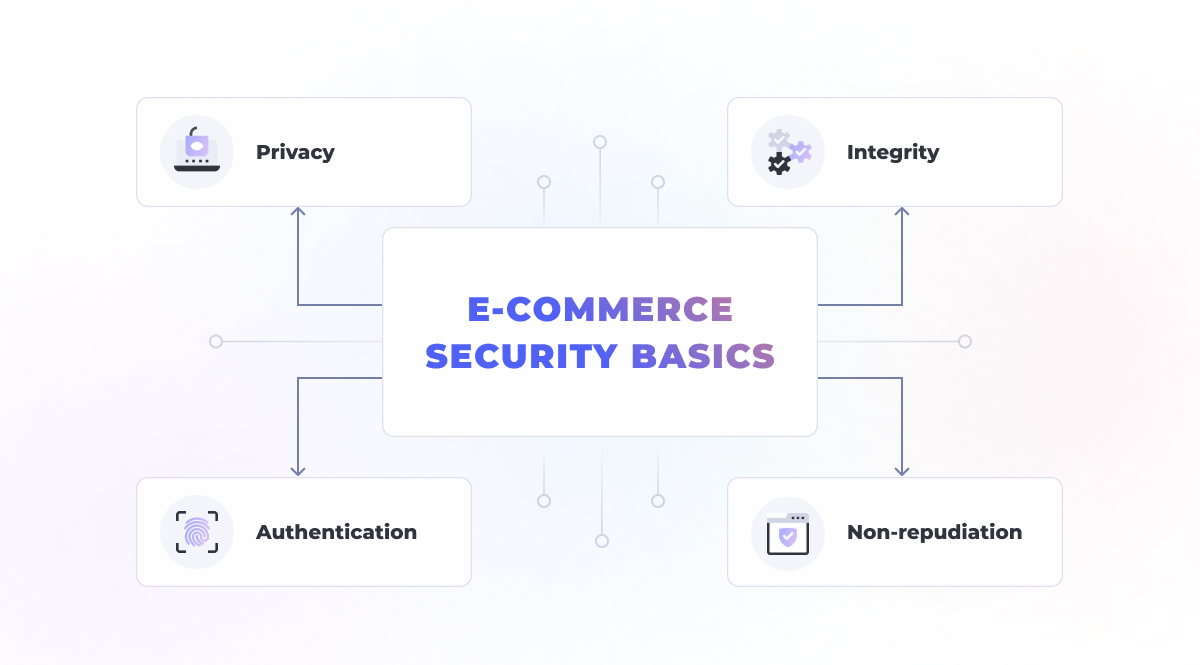
Understanding Security in E-commerce
In today’s digital landscape, security is a fundamental concern for both businesses and consumers engaging in e-commerce. The growth of online shopping has undeniably made life more convenient, but it has also given rise to various security challenges. This chapter delves into the essential aspects of security in e-commerce and how it relates to “Where To Buy” solutions.
The E-commerce Boom and Its Security Implications
The rapid growth of e-commerce platforms has brought numerous benefits, such as expanded markets, streamlined shopping experiences, and diverse product offerings. However, this widespread digital presence has also attracted the attention of cybercriminals. Understanding the security landscape is crucial for anyone involved in e-commerce, from business owners to customers.
The Different Facets of E-commerce Security
E-commerce security encompasses various elements, including data security, payment security, and user privacy. Let’s break down these critical facets:
Data Security: This involves safeguarding sensitive customer information, such as personal details and credit card numbers, from data breaches. A breach can lead to identity theft and financial losses, tarnishing a business’s reputation.
Payment Security: Securing payment transactions is essential for trust. Payment gateways must protect financial data during the authorization process, ensuring safe and reliable payments.
User Privacy: Respecting customer privacy is vital. Clear privacy policies and secure handling of personal information build trust, which is especially important in the “Where To Buy” solutions environment.
Security Challenges in E-commerce
E-commerce platforms face several security challenges:
Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals often use deceptive emails and websites to trick users into revealing their personal information or login credentials. Vigilance is required to prevent such attacks.
Data Breaches: Even the most robust security measures can’t guarantee 100% protection. Data breaches can occur due to various factors, including vulnerabilities in software or human error.
Fraudulent Activities: E-commerce businesses must combat various fraudulent activities, including fake product reviews, stolen credit card use, and account takeovers.
Regulatory Compliance: E-commerce companies must adhere to legal regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S., depending on the nature of their operations.
The Role of ‘Where To Buy’ Solutions in Security
“Where To Buy” solutions play a vital role in enhancing security in e-commerce. These solutions often integrate with e-commerce platforms, providing several security benefits:
Secure Purchase Links: “Where To Buy” solutions offer secure links to verified retailers, reducing the risk of customers falling prey to phishing scams.
Verified Retailers: They ensure that only legitimate retailers are listed, minimizing the chances of buying counterfeit or fraudulent products.
Privacy-Focused: Many “Where To Buy” solutions respect user privacy by not collecting unnecessary personal data, aligning with modern privacy regulations.
Secure Payment Options: These solutions often guide users to trusted retailers with secure payment methods, reducing the risk of payment fraud.
In this chapter, we’ve outlined the significance of security in the world of e-commerce and discussed how “Where To Buy” solutions contribute to a safer online shopping experience. The next chapters will delve deeper into specific aspects of e-commerce security and explore the unique advantages offered by these solutions.
Privacy Concerns in Online Shopping
In the digital age, online shopping has become an integral part of our lives. However, with the convenience of e-commerce comes the growing concern of privacy. Consumers want to enjoy a seamless shopping experience while keeping their personal information secure. This chapter explores the privacy concerns in online shopping, focusing on how they relate to “Where To Buy” solutions.
The E-commerce Privacy Landscape
Privacy is a fundamental right that extends into the digital realm. The rapid expansion of e-commerce has led to an increased exchange of personal data between consumers and businesses. Privacy issues in online shopping include:
Data Collection: E-commerce platforms collect a vast amount of data about users, such as their browsing history, purchase preferences, and even location.
Data Sharing: Many online retailers share customer data with third parties, including advertisers and data brokers, for targeted marketing.
Security Concerns: Data breaches can compromise the personal information of shoppers, leading to identity theft and financial loss.
Cookie Tracking: Online retailers often employ cookies to track user behavior, which can feel invasive and raise privacy concerns.
The Role of ‘Where To Buy’ Solutions in Privacy
“Where To Buy” solutions address many of these privacy concerns. Here’s how they contribute to a more private online shopping experience:
Reduced Data Collection: These solutions typically do not require users to provide personal information to find a product, reducing the data collected compared to traditional e-commerce platforms.
Privacy-Centric: “Where To Buy” solutions prioritize user privacy by not engaging in excessive data tracking or intrusive ad targeting.
Minimal Data Sharing: They typically don’t share user data with third parties, ensuring that consumers’ information remains within the confines of the solution.
Transparency: Many of these solutions clearly outline their privacy policies, giving users the confidence that their information is treated with care.
Secure Purchase Links: By guiding users to verified and trusted retailers, “Where To Buy” solutions minimize the risk of consumers clicking on malicious links or falling for phishing attempts.
Consumer Empowerment and Privacy
Privacy is not just a concern but also a matter of consumer empowerment. When consumers have more control over their personal data, they can make informed decisions about their online shopping experiences. “Where To Buy” solutions align with this idea by putting privacy back into the hands of consumers.
In essence, “Where To Buy” solutions provide an alternative to traditional online shopping, one that respects and values consumer privacy. This chapter has highlighted the privacy concerns surrounding e-commerce and the privacy-centric approach of “Where To Buy” solutions. The following chapters will delve deeper into various aspects of online shopping privacy and security.
Data Protection Regulations
In the digital age, data protection regulations have become increasingly important to safeguard the privacy and personal information of consumers engaged in online shopping. As “Where To Buy” solutions play a crucial role in this context, it is essential to explore the impact of data protection regulations on these solutions.
Data Protection Laws: An Overview
Data protection laws are designed to regulate the processing of personal data to protect individuals from privacy infringements. In recent years, several notable regulations have been enacted globally, including:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Implemented in the European Union, GDPR sets stringent standards for data protection and the rights of individuals regarding their personal data.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): California’s state law gives consumers the right to know what personal information is collected and how it’s used.
Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA): This U.S. law focuses on the online privacy of children under the age of 13.
Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): Enacted in Singapore, the PDPA governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data.
These regulations necessitate greater transparency and accountability from businesses, ensuring that consumers’ personal data is collected and processed in a secure and lawful manner.
How Data Protection Regulations Impact ‘Where To Buy’ Solutions
“Where To Buy” solutions, with their emphasis on respecting consumer privacy, are well-aligned with data protection regulations. Here’s how these regulations impact these solutions:
Consent Mechanisms: Data protection regulations often require obtaining explicit consent from consumers before collecting their data. “Where To Buy” solutions can integrate compliant consent mechanisms, ensuring users are fully aware of how their data will be used.
Data Minimization: Regulations like GDPR stress data minimization, meaning organizations should only collect and process data that is necessary for the intended purpose. “Where To Buy” solutions, which prioritize minimal data collection, naturally comply with this requirement.
Data Security: Regulations mandate the implementation of robust data security measures. “Where To Buy” solutions take data security seriously by directing users to reputable e-commerce platforms with secure transaction systems.
Data Transfer: Cross-border data transfer, which is a common practice in e-commerce, is subject to specific legal requirements under some data protection regulations. “Where To Buy” solutions can take measures to ensure compliant data transfers.
User Rights: Data protection regulations give users rights over their personal data, including the right to access, correct, or delete it. “Where To Buy” solutions can provide options for users to exercise these rights.
Privacy as a Competitive Advantage
As data protection regulations continue to evolve and become more comprehensive, businesses that prioritize data protection and privacy gain a competitive advantage. “Where To Buy” solutions, by embracing these regulations, enhance their credibility and trustworthiness, attracting consumers who are increasingly concerned about their data security.
Privacy Best Practices
Ensuring the privacy of consumers is paramount in the realm of e-commerce, especially for “Where To Buy” solutions. In this chapter, we’ll delve into some privacy best practices that these solutions can adopt to build trust, comply with regulations, and protect the personal information of users.
Transparent Data Policies
“Where To Buy” solutions should have transparent data policies, clearly stating what data is collected, how it is used, and with whom it may be shared. These policies should be easily accessible to users and expressed in plain language to ensure comprehension.
Secure Data Transmission
Secure data transmission is vital. Implementing encryption protocols (e.g., SSL) ensures that data exchanged between users and the solution is protected from interception. This encryption is especially crucial when transmitting sensitive information such as payment details.
Data Minimization
Adhering to data minimization principles, “Where To Buy” solutions should only collect and process data that is necessary for their intended purpose. Unnecessary data should not be stored or transmitted, reducing the risk of data breaches.
User Consent Mechanisms
To comply with data protection regulations, explicit user consent should be obtained before collecting personal information. Users must be informed about what data is being collected and why. Consent mechanisms should also make it easy for users to withdraw their consent.
Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments is essential to identify and rectify potential data security issues. These audits help in proactively addressing security concerns and ensuring robust data protection.
Anonymization and Pseudonymization
Sensitive data can be anonymized or pseudonymized to protect user privacy. Anonymization involves removing personally identifiable information, while pseudonymization replaces identifying information with non-identifiable data.
Strong Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is crucial to limit data access to authorized personnel only. Multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and proper training on data access procedures are some of the methods to control data access.
Rapid Data Breach Response
Despite robust preventive measures, data breaches can still occur. Therefore, “Where To Buy” solutions should have a well-defined and swift data breach response plan. This includes notifying affected parties and regulatory authorities promptly, as required by law.
Third-Party Vendor Evaluation
Many “Where To Buy” solutions rely on third-party vendors for various services. It is crucial to evaluate these vendors to ensure they adhere to the same rigorous privacy and security standards.
Privacy Impact Assessments
Before implementing new features or technologies, conducting privacy impact assessments (PIAs) can help identify and mitigate potential privacy risks. PIAs ensure that privacy considerations are an integral part of the solution’s development process.
Regular Training and Awareness
Well-informed employees are the first line of defense against data breaches. Regular training and awareness programs can help employees understand the importance of data protection and their role in safeguarding user privacy.
Privacy by Design
“Where To Buy” solutions should adopt a “privacy by design” approach, where privacy is considered at every stage of development. This proactive approach ensures that privacy features are built into the solution from the outset.
Adhering to these privacy best practices not only helps “Where To Buy” solutions build trust with users but also ensures compliance with data protection regulations. Privacy-conscious solutions are more likely to succeed in an era where users increasingly value their privacy and data security. The subsequent chapters will explore more about the technologies and strategies employed by these solutions to ensure privacy.

Security Measures in 'Where To Buy' Solutions
Security is of paramount importance in ‘Where To Buy’ solutions, which often deal with sensitive user data. In this chapter, we will explore the key security measures these solutions should adopt to protect user information and maintain trust.
Data Encryption: Data transmitted between users and the solution should be encrypted using technologies like SSL/TLS. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be deciphered.
Secure Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to ensure that only authorized users can access the solution. This adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
Regular Security Audits: Periodic security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential to identify and address potential weaknesses. Security audits help in staying one step ahead of potential threats.
Access Controls: Implement strict access controls, granting system access only to those who need it. Role-based access and the principle of least privilege help restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Utilize firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) can detect and alert administrators to potential security threats.
Security Patch Management: Keep all software, including the operating system and third-party applications, up-to-date with the latest security patches. Vulnerabilities in outdated software can be exploited by cybercriminals.
Security Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a robust security incident response plan. This plan should outline steps to be taken in case of a security breach, including notifying affected parties and regulatory authorities as required by law.
Regular Employee Training: Employees should be educated on security best practices. Security awareness programs can help employees recognize phishing attempts, social engineering, and other common security threats.
Secure Data Storage: Sensitive data should be securely stored, whether on servers or in the cloud. Encryption and strong access controls should be applied to protect data at rest.
Secure Third-Party Integrations: If the solution integrates with third-party services, it’s essential to ensure that these services follow robust security measures. Weaknesses in third-party integrations can expose vulnerabilities.
Authentication and Authorization: Implement proper user authentication and authorization mechanisms. Users should only have access to the data and functionality that is necessary for their roles.
Regularly Updated Security Policies: Security policies should evolve to address new threats and challenges. Regularly review and update these policies to stay current with security best practices.
Incident Monitoring and Response: Set up real-time monitoring of system logs and user activities. This enables the timely detection of unusual behavior that may indicate a security incident.
Secure Development Practices: Adopt secure development practices in the software development lifecycle. This includes code reviews, security testing, and adherence to secure coding guidelines.
Data Backups: Regularly back up data to protect against data loss due to security incidents. Ensure that backups are stored securely and can be quickly restored if needed.
Data Disposal: Properly dispose of data that is no longer needed. This includes both physical and digital data to prevent data breaches through discarded equipment or records.
User Education: Users should be informed about best security practices and the risks associated with their online activities. Regularly provide security tips and reminders to users.
Security measures are integral to the success and trustworthiness of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions. By implementing these best practices, these solutions can safeguard user data and provide a secure environment for consumers engaging in online shopping.
Secure Payment Processing
Secure payment processing is a critical aspect of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions. This chapter delves into the significance of ensuring payment security for both businesses and consumers. We’ll explore the mechanisms and best practices that help maintain the integrity of financial transactions.
PCI DSS Compliance: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance is essential for businesses that handle credit card transactions. Complying with PCI DSS standards ensures the secure handling of cardholder data.
Tokenization: Tokenization replaces sensitive card data with a unique token. This token can be used for payment processing without exposing the actual card information, making transactions more secure.
End-to-End Encryption: Implement end-to-end encryption for payment data, ensuring that it is protected throughout the entire transaction process, from the point of sale to authorization.
Two-Factor Authentication: Provide two-factor authentication for users during payment processing. This adds an extra layer of security, making it more challenging for unauthorized users to complete transactions.
Secure Payment Gateways: Use trusted and secure payment gateways that encrypt transaction data during online purchases. These gateways connect online merchants to payment processors.
Fraud Detection Systems: Employ advanced fraud detection systems that use machine learning and artificial intelligence to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions in real-time.
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits of payment systems and processes to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Address any issues promptly to ensure secure transactions.
Risk-Based Authentication: Implement risk-based authentication that assesses the risk associated with a particular transaction or user, requiring additional authentication when necessary.
Dynamic CVV Codes: Use dynamic Card Verification Value (CVV) codes that change periodically. These provide an additional layer of security as the CVV code is only valid for a short time.
Secure Mobile Payment Methods: If mobile payment methods are offered, ensure that they are secured with biometric authentication, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
Secure Storage of Payment Data: Businesses should store payment data securely, with access controls and encryption to protect sensitive financial information.
Regular Security Training: Train employees to recognize and respond to payment fraud and security threats. Human error is a common contributor to security breaches.
Payment System Monitoring: Implement 24/7 monitoring of payment systems to detect and respond to any unusual activities or security breaches promptly.
Data Retention Policies: Develop and enforce data retention policies that specify how long payment data should be stored and how it should be securely disposed of when no longer needed.
Dispute Resolution Processes: Have a well-defined process for handling payment disputes and chargebacks. Timely dispute resolution maintains trust with customers.
Secure payment processing is crucial for e-commerce businesses and ‘Where To Buy’ solutions. It not only protects sensitive financial information but also ensures a safe and reliable shopping experience for consumers. By following these best practices, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of payment fraud and data breaches.
User Authentication and Authorization
User authentication and authorization are fundamental components of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions, ensuring that access to sensitive information and critical functionalities is controlled and secured. In this chapter, we’ll explore the significance of user authentication and authorization and discuss best practices for implementing these security measures.
1. Password Policies:
- Implement robust password policies that require users to create strong, unique passwords.
- Encourage the use of password managers to generate and store complex passwords.
- Enforce password changes at regular intervals to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
- Require users to enable MFA, which adds an additional layer of security by verifying their identity through something they know (password) and something they have (e.g., a mobile device).
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Implement RBAC to define and manage user roles and permissions.
- Assign permissions based on job responsibilities, ensuring that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks.
4. Single Sign-On (SSO):
- Implement SSO to allow users to access multiple systems with a single set of credentials.
- This reduces the number of passwords users need to remember and streamlines access while enhancing security.
5. Session Management:
- Employ session management techniques to control and monitor user sessions.
- Implement session timeouts and automatic logouts after periods of inactivity.
6. Secure Authentication Protocols:
- Utilize secure authentication protocols like OAuth and OpenID Connect to ensure safe and reliable user authentication.
7. User Registration and Verification:
- Implement a secure user registration process that includes email verification or SMS confirmation to ensure that users are who they claim to be.
8. Continuous Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor user activities for suspicious behavior.
- Implement automated systems to detect and respond to anomalies or security breaches.
9. User Education:
- Educate users about best practices for securing their accounts, such as recognizing phishing attempts and using MFA.
10. User-Friendly Error Messages:
- Provide user-friendly error messages during the login process.
- Avoid revealing whether a username or password was incorrect to protect against unauthorized access attempts.
11. Secure Password Recovery:
- Implement a secure password recovery process, including identity verification to prevent unauthorized password resets.
12. Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities in the authentication and authorization systems.
- Address any weaknesses promptly.
User authentication and authorization are crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions. By implementing these best practices, businesses can protect user accounts, prevent unauthorized access, and provide a secure and trustworthy platform for users to access product information and make purchase decisions.
Incident Response and Data Breach Handling
In the world of e-commerce and ‘Where To Buy’ solutions, where sensitive customer data is regularly handled, incident response and data breach handling are critical components of any security strategy. This chapter explores the importance of these processes and outlines best practices for managing incidents and mitigating data breaches.
1. Define Incident Response Plans:
Have a well-documented incident response plan in place that outlines how the organization will react to security incidents.
2. Establish an Incident Response Team:
Form a dedicated incident response team comprising IT experts, legal advisors, and communication specialists.
3. Incident Identification and Categorization:
Implement tools and processes to quickly identify and categorize incidents by severity.
4. Containment Measures:
Once an incident is confirmed, take immediate containment measures to prevent it from spreading and causing further damage.
5. Eradication and Recovery:
After containment, focus on eradicating the root causes of the incident and restoring affected systems to normal operation.
6. Communication and Notification:
Develop a communication plan that addresses how and when to notify affected parties, including customers, regulatory authorities, and the public.
7. Compliance with Data Protection Regulations:
Ensure that all response efforts comply with relevant data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
8. Preserve Evidence:
Maintain a chain of custody for evidence related to the incident, which may be required in legal or regulatory investigations.
9. Post-Incident Review:
Conduct a thorough post-incident review to analyze what happened, what worked in the response, and what could be improved.
In the event of a data breach, it is crucial to act swiftly and effectively. Having a robust incident response plan can make the difference between a minor incident and a major security breach. A well-prepared and proactive approach to incident response and data breach handling not only helps to minimize damage but also maintains the trust of customers and business partners.
Conclusion and Future Trends
In the rapidly evolving landscape of e-commerce and ‘Where To Buy’ solutions, security and privacy considerations have become paramount. As we conclude this discussion on the impact of reviews and ratings on purchase decisions, as well as the importance of robust security practices in ‘Where To Buy’ solutions, let’s reflect on key takeaways and explore the future trends in this space.
Conclusion:
Reviews and ratings play a crucial role in shaping purchase decisions for consumers in the digital age. The trust and credibility established through user-generated content significantly influence a buyer’s choices. ‘Where To Buy’ solutions that incorporate these elements strategically not only enhance the customer experience but also boost conversion rates and sales. Privacy and data protection have emerged as fundamental aspects of online commerce, with consumers increasingly valuing businesses that safeguard their personal information. Implementing security measures, secure payment processing, and user authentication are prerequisites for earning the trust of online shoppers.
Key Takeaways:
The Power of User-Generated Content: User reviews and ratings can make or break a purchasing decision. Companies that encourage and manage user-generated content effectively can gain a competitive edge.
Privacy Matters: Consumers are increasingly concerned about their data privacy. Businesses must be transparent about how they handle customer information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Balancing Security and Convenience: Providing a secure shopping experience without compromising user-friendliness is a delicate balance. It’s essential to invest in robust security measures without creating obstacles for shoppers.
Incident Response Preparedness: Being ready to handle security incidents and data breaches is critical. Having an incident response plan in place can help mitigate the impact on your business and reputation.
Future Trends:
The future of ‘Where To Buy’ solutions and e-commerce security and privacy is likely to see several key trends:
AI-Driven Personalization: Artificial intelligence will play a more prominent role in tailoring product suggestions and enhancing the shopping experience, further influencing purchase decisions.
Stricter Data Regulations: As data privacy concerns grow, we can anticipate more stringent data protection regulations globally, necessitating stronger compliance efforts.
Biometric Authentication: Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, are likely to become more prevalent in online transactions for a seamless yet secure user experience.
Blockchain for Trust: Blockchain technology may be increasingly used to create transparent and immutable records of reviews and ratings, reducing the risk of manipulation.
Cybersecurity Innovations: The cybersecurity landscape will continue to evolve, with businesses adopting advanced threat detection and prevention measures to safeguard customer data.
Secure Payment Methods: Emerging payment methods and cryptocurrencies will bring both opportunities and challenges to online payment security.
Consumer Education: Educating consumers about online security and privacy issues will become a shared responsibility for businesses and authorities.
As technology advances and consumer expectations continue to shift, ‘Where To Buy’ solutions must adapt to remain competitive and trustworthy. Those that proactively address these evolving trends and prioritize the security and privacy of their customers are likely to thrive in the e-commerce industry.
In conclusion, the impact of reviews and ratings on purchase decisions is undeniable, and the implementation of security and privacy measures in ‘Where To Buy’ solutions is non-negotiable. By staying ahead of emerging trends and putting the customer’s trust at the center of their strategies, businesses can build a sustainable and successful future in the digital marketplace.
FAQs
1 Why are online reviews and ratings so important for e-commerce businesses?
Online reviews and ratings serve as social proof and help build trust with potential customers. They provide insights into the quality and performance of products or services, influencing purchase decisions and boosting sales.
2 How can businesses encourage customers to leave reviews and ratings?
To encourage reviews, businesses can send post-purchase emails, offer incentives, and create user-friendly review submission processes. Responding to reviews, whether positive or negative, also encourages more customers to share their experiences.
3 What should e-commerce businesses do to protect customer data and privacy?
To protect customer data and privacy, businesses should implement robust security measures, follow data protection regulations, and be transparent about data handling practices. Regular security audits and incident response plans are also essential.
4 How can businesses maintain a balance between user privacy and collecting valuable customer data for improving services?
To strike a balance, businesses should clearly communicate their data collection practices, obtain user consent, and only collect data necessary for improving services. Anonymizing data and offering opt-out options can also respect user privacy.
5 What are some best practices for managing online reviews and ratings effectively?
Effective review management includes responding to reviews promptly, addressing negative feedback constructively, and monitoring reviews on multiple platforms. Utilizing feedback for product or service improvements can also enhance the overall customer experience.
